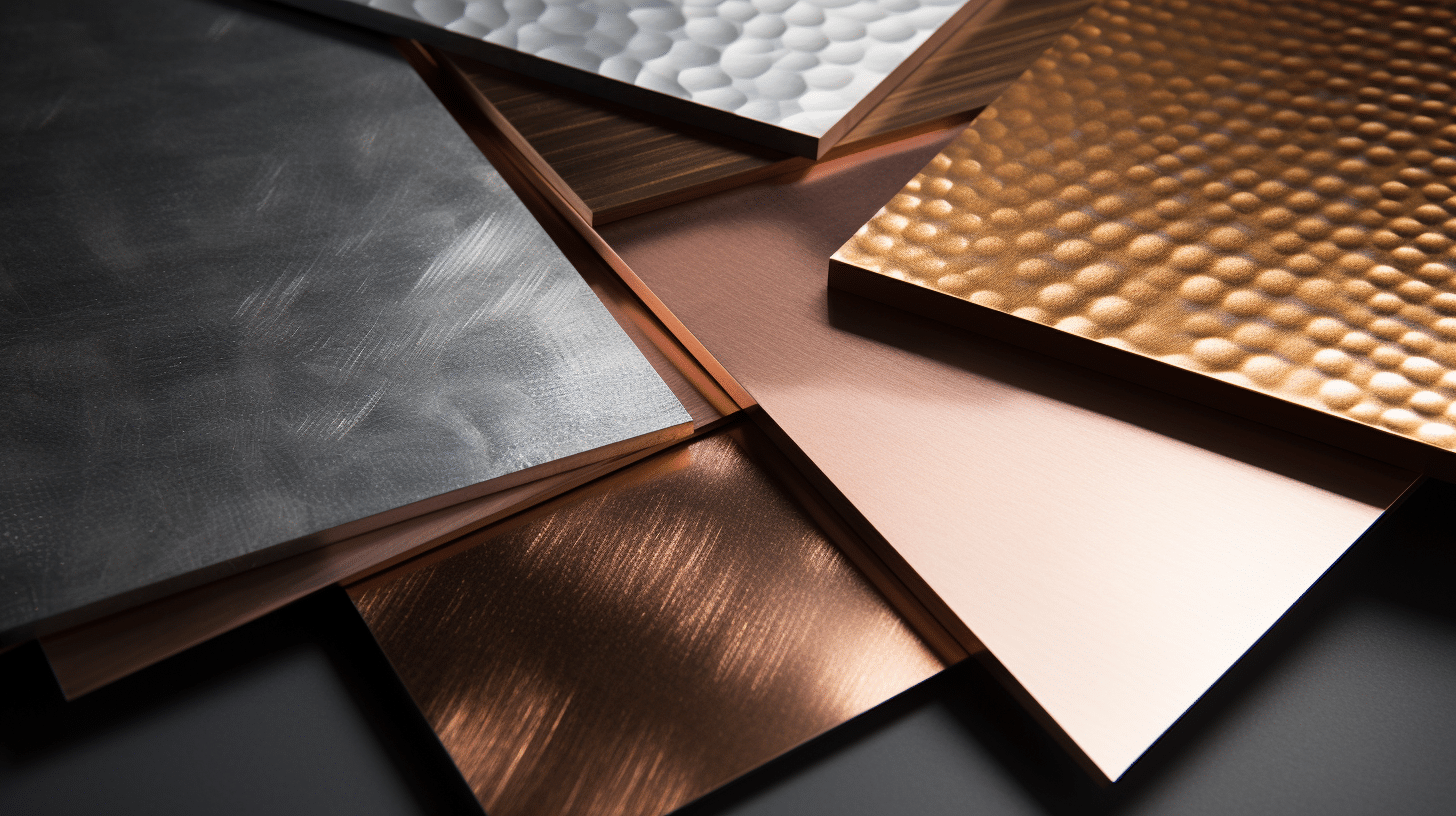
Metal processing plays a crucial role in a wide range of industries, from automotive and aerospace applications to electrical components and medical instruments. Therefore, selecting the right material for your sheet metal fabrication project ensures the end product’s success. In this article, we explore the key factors to consider when choosing a material for sheet metal parts.
Types of Sheet Metal Materials
The choice of sheet metal material is a crucial decision in the design process. Each type of material offers its own set of advantages and disadvantages, making it essential for designers and engineers to consider the specific requirements of the project, such as corrosion resistance, strength, weight, and the complexity of the desired shapes.
Metals and Alloys
Sheet metals derived from various metals and alloys offer a wide range of properties to cater to different applications:
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is a versatile material known for its exceptional corrosion resistance. This property makes it an ideal choice for applications exposed to corrosive chemicals, harsh environments, and frequent moisture contact. Stainless steel is available in different grades, each offering specific corrosion resistance levels and mechanical properties. This variety allows designers to select the best grade for their particular needs. Common applications for stainless steel include kitchen appliances, medical instruments, and marine components.
- Benefits: Excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for corrosive environments.
- Drawbacks: Higher material costs compared to other options.
Carbon Steels
Carbon steels are widely used for sheet metal parts due to their strength and cost-effectiveness. They come in various forms, such as mild steel and galvanized steel. Mild steel is a popular choice for structural components in construction and general-purpose applications. Galvanized steel has a protective zinc coating that enhances its corrosion resistance, making it suitable for outdoor and industrial applications.
- Benefits: Strong and cost-effective.
- Drawbacks: Susceptible to corrosion without proper coating.
Nickel-Silver Alloys
Nickel-silver alloys are specialized materials primarily chosen for their excellent electrical conductivity. They are a common choice for electrical components like switches, connectors, and conductive springs. These alloys also contain a protective ingredient that helps prevent corrosion. While not as widespread as stainless steel or carbon steel, nickel-silver alloys serve a critical role in specific applications.
- Benefits: Excellent electrical conductivity and a protective alloy ingredient.
- Drawbacks: Limited use in specific applications.
Soft Metals
Soft metals, like zinc and aluminum, are valued for their unique characteristics, especially when weight reduction is a critical factor:
Zinc
Zinc is a lightweight material commonly used in sheet metal applications where reducing weight is essential. It is easily machinable and can be formed into complex shapes, making it ideal for intricate designs. Zinc sheet metal is often employed in automotive components, die-casting molds, and decorative ornaments.
- Benefits: Offers a protective coating that enhances corrosion resistance.
- Drawbacks: Not as durable as other corrosion-resistant materials.
Aluminum
Aluminum is renowned for its low density, making it an excellent choice for applications where weight reduction is a priority. It is highly machinable and can be formed into intricate shapes, making it versatile for various industries. Aluminum sheet metal is commonly used in aerospace components, consumer electronics, and automotive parts where lightweight and durable solutions are required.
- Benefits: Lightweight and suitable for intricate designs.
- Drawbacks: Limited strength compared to steel.
Considerations for Material Selection
Material selection for sheet metal parts is a multifaceted process that requires careful consideration of various factors. By analyzing mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, weight, shape, tolerance, finishing options, and application-specific requirements, you can make an informed decision that ensures the success and longevity of your sheet metal components.
Mechanical Properties
- Tensile Strength: Tensile strength measures a material’s ability to withstand pulling forces without breaking. Understanding this property is crucial, as it helps determine whether the material can bear the load and stress the application demands. For heavy-duty applications, materials with high tensile strength are preferred.
- Yield Strength: Yield strength represents the point at which a material begins to deform plastically under stress. It’s essential to know this value to ensure that the material doesn’t deform or fail prematurely during use.
- Shear Strength: Shear strength is important in applications where forces act parallel to the material’s surface. Knowing the shear strength is vital to prevent failures due to sliding or shearing forces.
Corrosion Resistance
Consider the environment in which the sheet metal part will be used. Some materials offer excellent corrosion resistance, making them ideal for applications exposed to moisture, chemicals, or harsh outdoor conditions. Stainless steel, for instance, is renowned for its resistance to rust and corrosion, making it an excellent choice for marine and chemical industry applications.
Weight Reduction
In certain industries, such as aerospace and automotive, reducing weight is critical for fuel efficiency and performance. Materials like aluminum are favored for their lightweight properties while still offering adequate strength for the intended purpose.
Shape and Size
Different materials behave differently when it comes to forming complex shapes or maintaining the original shape. Some materials, like aluminum, are highly malleable and can be easily shaped into intricate designs, making them suitable for applications with unique geometric requirements. Others, like high-strength steel, excel at retaining their shape under load and are preferred for structural components.
Tight Tolerances
Precision is vital in many manufacturing processes. Some sheet metals offer tighter tolerances, allowing for more accurate and consistent production. For applications where tight tolerances are a requirement, the choice of material can impact the quality of the final product.
Finishing Options
Material choice can influence the surface finish of sheet metal parts. Some materials inherently possess qualities like natural corrosion resistance or aesthetic appeal, while others may require additional coatings or finishes to meet specific requirements. The choice of finish can impact not only the appearance but also the longevity of the part.
Application Requirements
Every application has unique demands that may include electrical conductivity, high strength, or resistance to specific chemicals. It’s crucial to consider the specific needs of your application to select a material that aligns with those requirements. For example, electrical components often require materials with good conductivity, while aerospace applications demand materials with high strength and low weight.
Can a Contract Manufacturer Assist with Product Design and Development?
Examples of Sheet Metal Materials Used in Various Applications
- Automotive Industries: Steel sheet metal parts are widely used for vehicle frames and structural components due to their strength.
- Aerospace Applications: Aerospace parts often use aluminum for its lightweight properties and strength.
- Electrical Components: Copper sheet metal is preferred for electrical components due to its excellent conductivity.
- Medical Instruments: Stainless steel is common in the medical industry, thanks to its corrosion resistance and ease of sterilization.
- HVAC Systems (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning): Galvanized steel sheet metal is often employed in HVAC ductwork due to its durability and corrosion resistance.
- Electronics Enclosures: Aluminum sheet metal is a common choice for enclosures in the electronics industry because of its lightweight and protective properties.
- Architectural Cladding: Stainless steel and aluminum sheet metals are favored for architectural cladding to achieve an aesthetically pleasing and durable exterior.
- Kitchen Appliances: Stainless steel is a popular material for kitchen appliances like refrigerators and ovens due to its clean and corrosion-resistant surface.
- Automotive Exhaust Systems: Aluminized steel sheet metal is used in automotive exhaust systems for its heat resistance and corrosion protection.
- Solar Panels: Thin aluminum sheet metal is frequently used as the substrate for solar panels, balancing strength and weight.
- Industrial Machinery: Carbon steel sheet metal is utilized in various industrial machinery due to its strength and cost-effectiveness.
Metal Processing Services
At Alpha Contract Manufacturing Group, we are innovative leaders in the realm of metal processing services. Through collaborative partnerships with our extensive network of local metalworking companies, we are equipped to manage a diverse spectrum of projects with ease and deliver an all-in-one solution for the intricate challenges of the metal processing industry.
We have the manpower and know-how to handle the design, fabrication, deployment, or maintenance of a broad range of metal-based products, offering seamless and unwavering support at every phase. Moreover, we go above and beyond metal processing to provide you with a complete solution for contract manufacturing by offering the following services:
- Industrial painting services
- Machining services
- Plastic manufacturing services
- Wood processing services
- Rubber processing services
- Laser cutting services
- Industrial welding services
- Electromechanics services
- Composite manufacturing services
- Industrial automation services
- Assembly manufacturing services
Become our partner and ensure that your project receives the utmost attention, from its inception to the delivery of the final product.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a “bend radius” in sheet metal bending?
A bend radius is the minimum radius at which a sheet metal part can be bent without causing deformation or cracks in the material. It’s a critical consideration to ensure the part’s integrity.
What are “bend lines” in sheet metal fabrication?
Bend lines are marks or guidelines on the sheet metal that indicate where the bending process should occur. These lines are essential for precise and consistent bending.
What tools are commonly used for sheet metal bending?
Various tools are used for sheet metal bending, including press brakes, rollers, and specialized hand tools, depending on the complexity of the bends and the material thickness.
How does laser cutting affect the edges of sheet metal pieces?
Laser cutting provides clean, precise edges on sheet metal pieces, minimizing the need for additional finishing work. It’s an efficient method for cutting and shaping sheet metal.
What is the role of powder coating in the sheet metal manufacturing process?
Powder coating is a finishing process used to enhance the appearance and durability of sheet metal parts. It involves applying a dry powder that adheres electrostatically to the metal surface before curing in an oven.
Can thicker materials be bent using the same process as thinner materials?
Thicker materials often require more force and specialized tools for bending. The bending process may need to be adjusted to accommodate the increased material thickness.
How does laser cutting impact the manufacturing process of sheet metal parts?
Laser cutting is a versatile and efficient manufacturing method that allows for intricate designs and precise cuts, reducing the need for secondary processing steps.